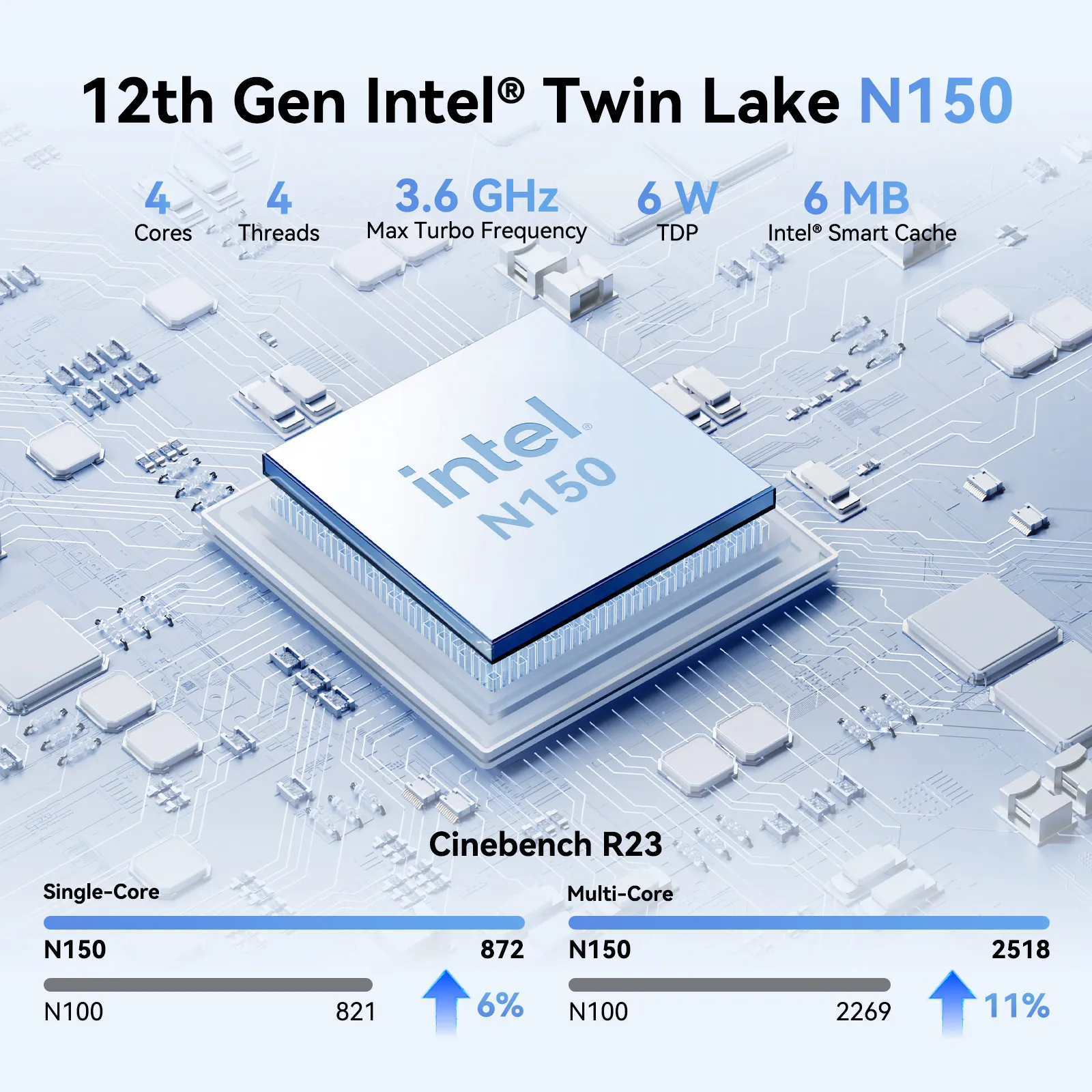
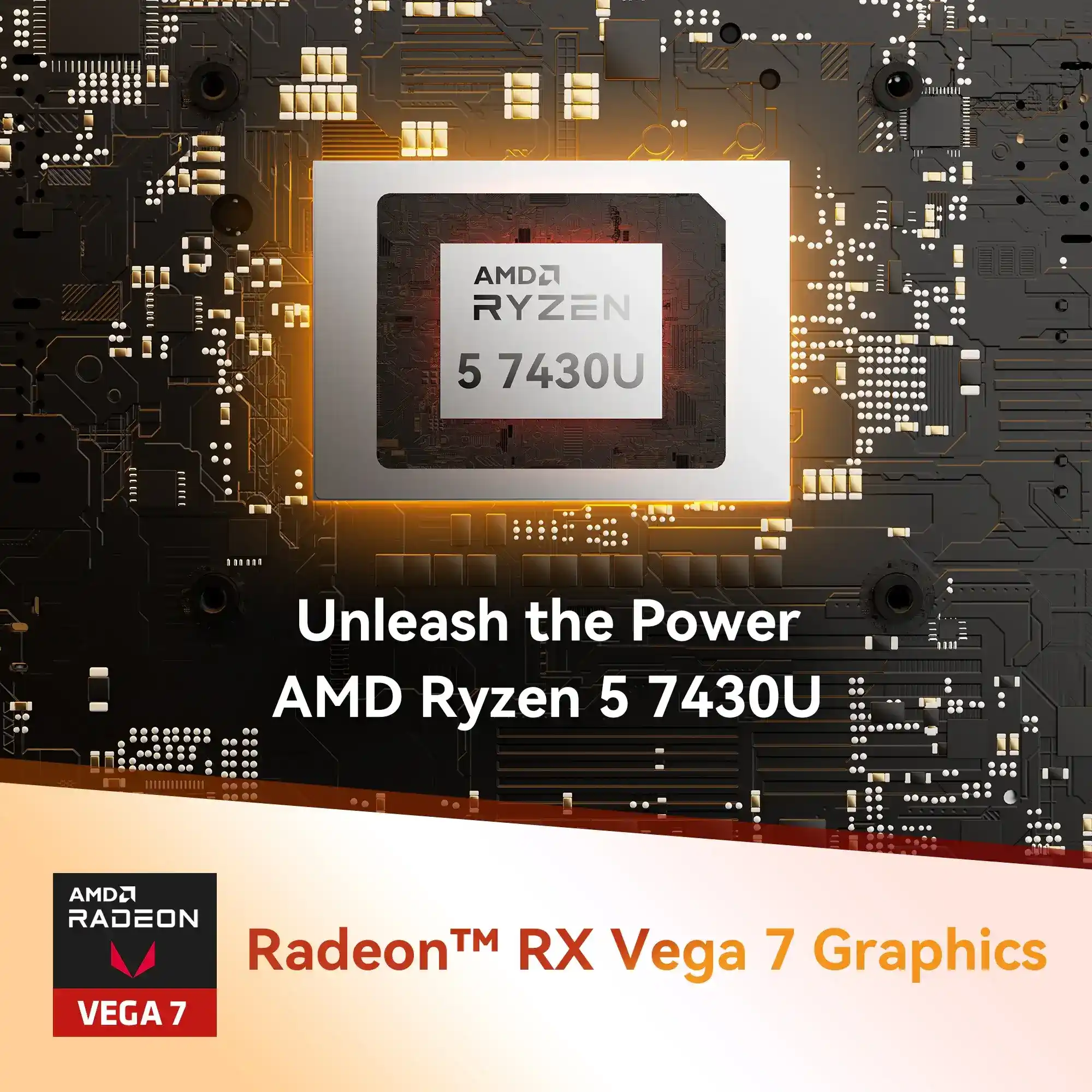
In the realm of computing, you often come across the acronym “TDP,” which stands for Thermal Design Power.
TDP is a critical parameter used to measure and manage the amount of heat generated by a computer component, such as a processor or graphics card.
When it comes to Mini PCs, This parameter plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and efficiency of these compact computing machines.
1. What is TDP? A Basic Definition
TDP stands for Thermal Design Power, and it is a measure of the heat-generating capacity of a computer hardware component. It is the maximum amount of heat a computer chip, such as a CPU or GPU, can produce under normal operating conditions.
Every electronic component generates heat, including microprocessors. Computer microprocessors typically utilize a substantial amount of power that can cause them to overheat if not adequately controlled. Typically, the Thermal Design Power or TDP refers to the maximum amount of power a computer CPU can consume within a given period without overheating.
In simple terms, TDP is a measure of the amount of power that a system can handle without overheating or causing damage to the internal components. The higher the TDP, the more power a mini PC can handle, but it also means that it produces more heat, which requires a more robust cooling system to maintain the performance.
2. Is TDP the same as a power draw?
It’s important to note that TDP is not the same as power draw. Power draw refers to the actual amount of power consumed by a component in watts, whereas TDP is a measure of the amount of heat a component can create.
Some people assume that TDP and power draw are two interchangeable terms. However, this is not entirely accurate. TDP refers to the power consumption of a CPU or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) at full load, whereas power draw may vary depending on usage scenarios.
For instance, a Mini PC in idle mode will consume less power than one under full load. Additionally, the Mini PC’s components’ quality and configuration will determine the power consumed, which in turn affects TDP.
3. Does higher TDP mean better performance?
it’s not always true that higher TDP means better performance. TDP is a measure of thermal headroom, which is the maximum amount of heat that a component can produce under normal operating conditions. A CPU or GPU with a higher TDP can generate more heat, but this doesn’t necessarily mean it performs better.
The mini PC’s overall performance depends on a variety of factors, such as the processor’s clock speed, the number of cores, the amount of cache, the graphics card, the storage device and capacity, and the installed RAM. Additionally, the mini PC’s operating environment, such as ambient temperature, airflow, and ventilation, also plays a significant role in the mini PC’s performance.
Many people associate a higher TDP with better performance; however, this is not always the case. While higher TDP CPUs are typically more powerful, they also generate more heat, which can lead to potential cooling issues, noise, and shorter lifespan.
Mini PCs with higher-powered CPUs like Intel Core i7, i9, or AMD’s Ryzen 7, 9, or Threadripper series may reach higher clock speeds, but this does not always translate to better performance, especially for casual users.
Recommended TDP for different usage scenarios
Here are some recommended TDP values for specific usage scenarios.
For office work, browsing the web or streaming, low-end Mini PCs with CPU TDPs between 4-25 watts are adequate.
For creative tasks, like photo or video editing, programming, or running Virtual Machines, a Mini PC requires a higher TDP CPU, projecting moderate workload performance. Thus, a CPU with a TDP between 25-45 watts is appropriate.
For Gaming or other intensive workloads requiring higher CPU and Graphics Processing, a Mini PC’s TDP should be between 50-95 watts. Such high-performance chips include the Intel Core i7 or i9 series, or AMD’s Ryzen 7 or 9 series, paired with dedicated graphics or an external GPU dock.
Conclusion
If you’re interested in exploring low-TDP computing solutions, we recommend checking out the range of mini PCs available from GEEKOM.
These mini PCs are designed to offer powerful performance while maintaining low TDP values, making them ideal for small form factor systems and energy-efficient computing.